 Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.
Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. electrostatics, the study of electromagnetic phenomena that occur when there are no moving charges—i.e., after a static equilibrium has been established. Charges reach their equilibrium positions rapidly, because the electric force is extremely strong.
electrostatics, the study of electromagnetic phenomena that occur when there are no moving charges—i.e., after a static equilibrium has been established. Charges reach their equilibrium positions rapidly, because the electric force is extremely strong.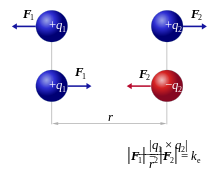 Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law [1] of physics that calculates the amount of force between two electrically charged particles at rest. This electric force is conventionally called the electrostatic force or Coulomb force. [2] Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. Coulomb ...
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law [1] of physics that calculates the amount of force between two electrically charged particles at rest. This electric force is conventionally called the electrostatic force or Coulomb force. [2] Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. Coulomb ...